The Essential Role of Instruments for Surgery in Modern Medicine
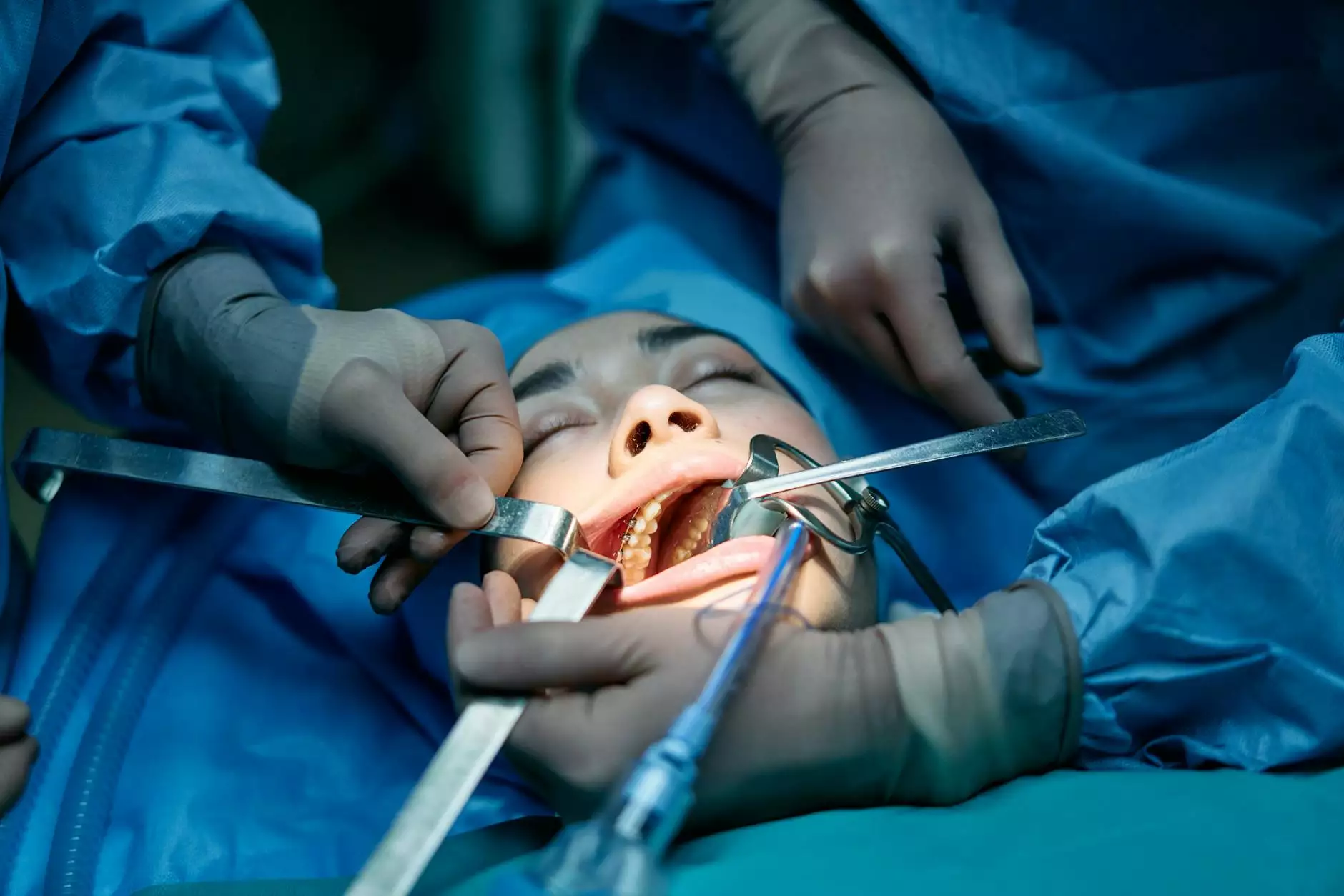
In the intricate world of healthcare, the term instruments for surgery encompasses a vast array of tools that are fundamental in procedures aimed at diagnosing, repairing, and treating various medical conditions. As we delve into this critical aspect of the medical field, we aim to provide comprehensive insights into the types, uses, and advancements in surgical instruments. This article aims to shed light on how these instruments revolutionize patient care and enhance surgical outcomes.
Understanding Surgical Instruments
Surgical instruments can be defined as tools or devices specifically designed to aid in performing surgical procedures. They are categorized based on their functionality, structure, and purpose. A comprehensive understanding of these instruments is essential for both medical professionals and patients alike.
Types of Surgical Instruments
The array of instruments for surgery can be broadly classified into several categories, each serving a distinct purpose:
- Cutting Instruments: These include scalpels, scissors, and knives, which are used for incisions and excisions.
- Grasping Instruments: Forceps and clamps fall under this category, allowing surgeons to hold or manipulate tissues.
- Hemostatic Instruments: Tools like hemostats are crucial for controlling bleeding during procedures.
- Retractors: These instruments help to hold back tissues and provide access to surgical sites.
- Suction Devices: Used to clear blood and other fluids from the surgical field, enhancing visibility.
- Electrosurgical Instruments: Devices such as diathermy units that cut tissue and coagulate blood using electrical current.
The Importance of Quality in Surgical Instruments
The efficacy of surgical procedures greatly depends on the quality of the instruments used. High-quality surgical instruments ensure precision, safety, and durability. They must meet stringent regulatory standards and be manufactured with optimal materials to withstand the rigors of surgical procedures.
Material Considerations
Most surgical instruments are made from materials that provide strength while minimizing risks of infection. The common materials include:
- Stainless Steel: Known for its corrosion resistance and strength, stainless steel is the primary material used in surgical instruments.
- Titanium: Lightweight and exceptionally strong, titanium instruments are favored for their durability and compatibility with imaging techniques.
- Non-stick Coatings: Some instruments feature advanced coatings that reduce friction and enhance performance.
Innovations in Surgical Instruments
With the rapid advancement of technology, the field of surgical instruments has seen significant innovations. These advancements lead to enhanced safety, efficiency, and outcomes of surgical procedures.
Minimally Invasive Instruments
The emergence of minimally invasive surgery techniques has necessitated the development of specialized instruments that allow surgeons to perform complex procedures through smaller incisions. Examples include:
- Laparoscopic Instruments: Designed for use in laparoscopic surgery, these instruments include trocars and cannulas, which facilitate access to the abdominal cavity.
- Robotic Surgical Instruments: With the integration of robotics in surgery, instruments can be controlled with precision, enhancing the surgeon’s capabilities.
Smart Surgical Instruments
Recent innovations have introduced "smart" surgical instruments equipped with sensors and connected technologies. These advancements enable real-time monitoring of parameters such as temperature and pressure, aiding surgeons in making informed decisions during procedures.
Regulatory Standards and Safety
The manufacturing and use of instruments for surgery are governed by strict regulatory standards to ensure safety and effectiveness. Bodies such as the FDA in the United States play a crucial role in overseeing the approval and regulation of surgical instruments.
Compliance with standards such as ISO 13485, which pertains to quality management systems for medical devices, is essential for manufacturers to demonstrate their commitment to producing high-quality instruments.
Choosing the Right Surgical Instruments
For medical professionals, selecting the right instruments for surgery is paramount. Various factors influence this choice, including:
- Procedure Requirements: The type of surgery dictates the specific instruments needed.
- Patient Factors: Individual patient needs, such as anatomical considerations and medical history, play a significant role.
- Surgeon Preference: Personal experience and preferences of the surgeon also affect instrument selection.
Training and Familiarization
Instruments for surgery require proper training and familiarization. Surgeons and surgical teams must understand the functionality, handling, and maintenance of each instrument. Comprehensive training programs and simulation-based learning are essential for ensuring proficiency and safety in surgical settings.
The Future of Surgical Instruments
The future of surgical instruments is intertwined with the evolution of technology and medical practices. Innovations such as 3D printing offer possibilities for creating customized instruments tailored to the specific needs of surgeries. Additionally, as the trend towards personalization in medicine expands, instruments adapted for individual patients may become a commonplace reality.
Artificial Intelligence in Surgery
Artificial intelligence (AI) is making waves in the healthcare sector, including the design and use of surgical instruments. AI could facilitate the enhancement of precision instruments, as well as provide predictive analytics that can inform procedural decisions.
Ensuring Proper Maintenance and Sterilization
Maintenance and sterilization of surgical instruments are critical for preventing infections and ensuring instrument longevity. Proper protocols must be followed:
- Cleaning: Immediately after use, instruments should be cleaned to remove blood and tissue debris.
- Disinfection: Instruments must undergo disinfection processes before sterilization to further minimize infection risks.
- Sterilization: Common sterilization methods include autoclaving, chemical sterilants, and gas sterilization.
Final Thoughts on Instruments for Surgery
In conclusion, instruments for surgery hold a fundamental position in modern healthcare. Their diverse roles span across various disciplines, impacting patient care directly. From high-quality materials to cutting-edge technologies, the evolution of surgical instruments underscores their importance in achieving successful surgical outcomes. By staying informed about advancements and best practices in the use and maintenance of these instruments, healthcare professionals can significantly enhance their contributions to patient health and safety.
For more information on high-quality surgical instruments and to explore our extensive catalog, visit new-medinstruments.com.









