Understanding Blood Clots in the Lower Leg: A Comprehensive Guide

Blood clots in the lower leg represent a significant health issue that can impact individuals of all ages. These clots, known medically as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), can lead to serious complications if left untreated. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, risks, treatments, and preventive measures for blood clots in the lower leg, providing you with the information needed to understand and manage this condition effectively.
What Are Blood Clots?
A blood clot is a mass of blood that has changed from liquid to a solid state. This process is crucial for healing, as it prevents excessive bleeding when you get injured. However, when a clot forms without an apparent cause, particularly in the deep veins of the legs, it can lead to serious complications.
Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. This condition is particularly concerning because if the clot dislodges, it can travel to the lungs and cause a pulmonary embolism, which is a life-threatening condition. It is crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms of DVT early to prevent severe outcomes.
Causes of Blood Clots in the Lower Leg
Understanding the causes of blood clot in the lower leg helps in recognizing individuals at risk. Several factors contribute to the development of DVT, including:
- Prolonged Immobility: Long periods of inactivity, such as during long flights or bed rest after surgery, can lead to blood pooling and clot formation.
- Injury or Surgery: Damage to veins from injury or surgical procedures can trigger clot formation as part of the healing process.
- Medical Conditions: Certain diseases, such as cancer, heart disease, or autoimmune disorders, increase the risk of clotting.
- Hormonal Factors: Hormonal changes due to pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy can contribute to increased clot risk.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put additional pressure on the veins in the legs, increasing the likelihood of DVT.
- Age: Risk increases with age, especially for those over 60 years old.
Symptoms of Blood Clots in the Lower Leg
Recognizing the symptoms of a blood clot in the lower leg is critical for timely intervention. Symptoms may include:
- Swelling: The affected leg may swell noticeably.
- Pain: Often described as a cramp or soreness in the calf or thigh.
- Red or Discolored Skin: The skin over the clot may appear reddish or have a bluish tint.
- Warmth: The area may feel warm to the touch compared to the other leg.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly.
Complications of Blood Clots
The most severe complication associated with a blood clot in the lower leg is a pulmonary embolism (PE). This occurs when a clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, blocking a pulmonary artery. Symptoms of PE include:
- Shortness of Breath: Sudden difficulty breathing or feeling winded.
- Chest Pain: Sharp pain that may worsen with deep breaths or coughing.
- Coughing Up Blood: This can be a sign of a serious pulmonary issue.
Immediate medical treatment is crucial if these symptoms develop as they may indicate a life-threatening condition.
Diagnosing Blood Clots
Diagnosis of DVT involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging. Common methods to diagnose blood clots include:
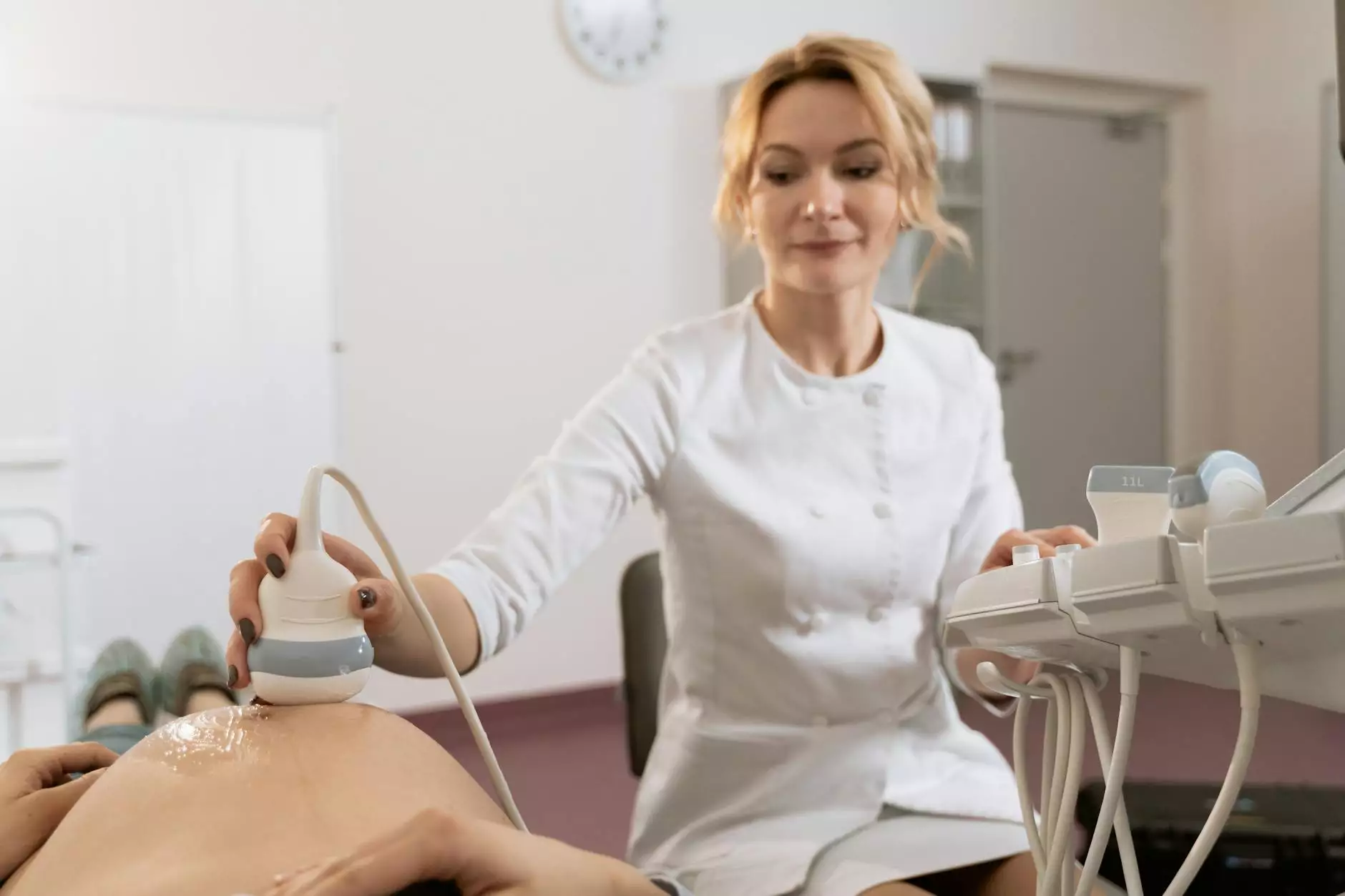
- Ultrasound: The most common test, where sound waves create an image of the blood flow in the leg.
- Blood Tests: D-dimer tests measure the presence of substances that are released when a blood clot breaks up.
- Venography: An X-ray test that can provide images of veins after injecting a contrast dye.
Treatment Options for Blood Clots in the Lower Leg
Effective treatment is essential in managing blood clots in the lower leg. The treatment plan may depend on the clot's size, location, and the individual's overall health. Common treatment options include:
- Anticoagulant Medications: Also known as blood thinners, these medications help prevent further clotting and allow the body to gradually dissolve the existing clot.
- Thrombolytics: In severe cases, stronger medications are used to dissolve clots quickly, but they carry a higher risk of bleeding.
- Compression Stockings: Graduated compression stockings can help reduce swelling and prevent complications associated with DVT.
- Inferior Vena Cava Filters: In certain cases, a filter may be placed in the inferior vena cava to catch any traveling blood clots before they reach the lungs.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to remove a dangerous clot.
Preventing Blood Clots
Prevention is key to avoiding the risks associated with DVT. Here are some effective strategies:
- Maintain Mobility: Avoid long periods of immobility; if sitting for long, take breaks to stretch and move around.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to help keep your blood from becoming too thick.
- Healthy Weight: Maintain a healthy weight through balanced diet and regular physical activity.
- Avoid Smoking: Tobacco use increases the risk of clot formation, so quitting smoking is beneficial.
- Wear Compression Garments: For individuals at risk, wearing compression stockings can improve circulation.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is essential to seek immediate medical attention if you suspect you have a blood clot in the lower leg. Key indicators include:
- Severe swelling or pain in one leg: This could indicate a clot is forming.
- Symptoms of pulmonary embolism: Shortness of breath, chest pain, or coughing up blood require urgent care.
Conclusion
Blood clots in the lower leg can pose serious health risks; however, with timely recognition, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment, these risks can be managed effectively. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk of DVT and its complications. Always consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about blood clots or your health.
Resources for Further Learning
For more information on blood clots and vascular health, consider visiting the following resources:
- trufflesveinspecialists.com - Experts in vascular medicine and preventative care.
- CDC: Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) - Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- Mayo Clinic: Deep Vein Thrombosis - Comprehensive medical insights on DVT.